If you’re in the business of producing plastic parts and like components, you’re probably familiar with 3D printing and injection molding. These processes each have their own advantages and can be used independently or together, as a team.
3D printing can be added to machine mechanisms, creating plastic parts by building up layers of material. Injection molding creates plastic parts through a different manufacturing process, one that uses a mold to shift and harden plastic into a sellable end product.
One thing you have to keep in mind while comparing the two is that they are very different. Advantages of each will be laid out below for your analysis.
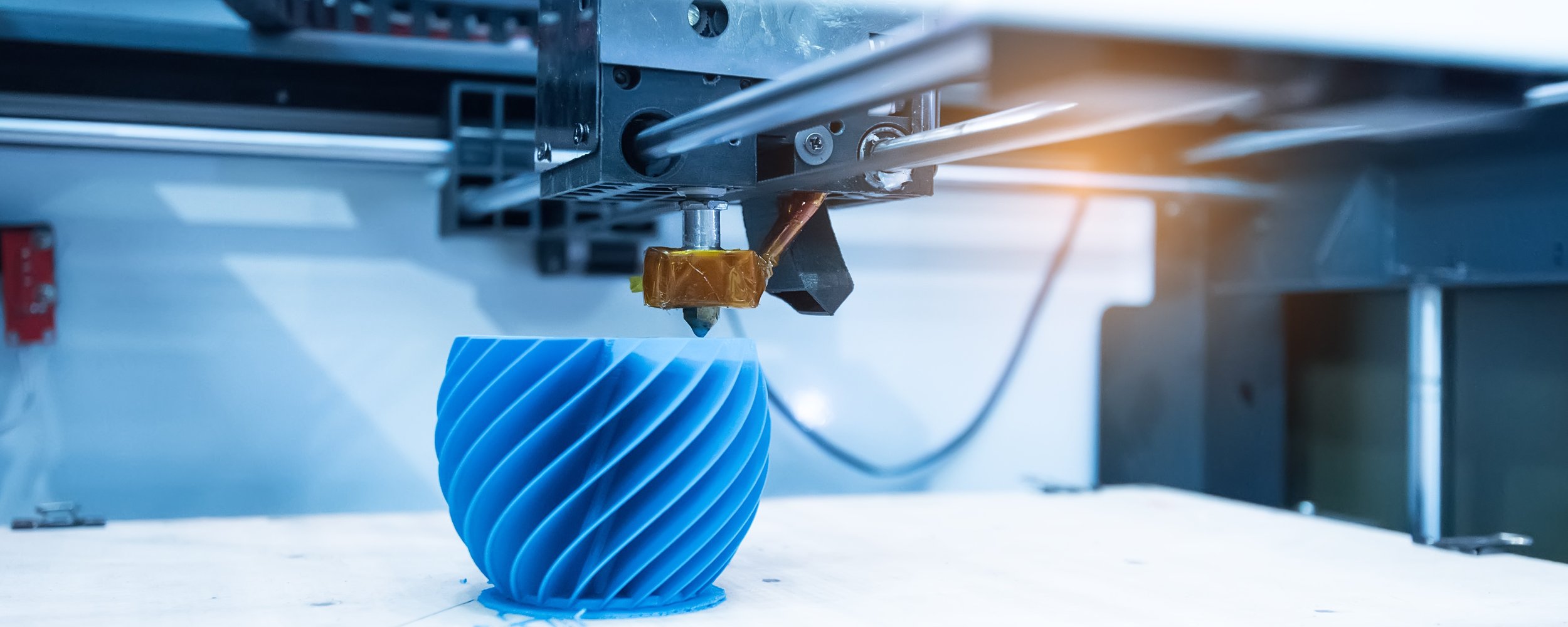

3D Printing Advantages
All in all, 3D printing offers one of the fastest turnaround times for manufacturers, oftentimes clocking in at one to two weeks. If you’re looking for fast production, or you need designs to go through frequent changes, 3D printing may be your best bet.
Additional advantages include:
- Low entry cost → Desktop versions of 3D printers with supplies definitely costs less money than what you would spend for injection molding equipment.
- Easy made design changes → Design changes can happen with a quick click of the right button, even in the middle of production. This can stop a flaw in its midst before you mass produce a product you don’t want to sell.
- Easy made intricate designs → Producing parts layer-by-layer means that you can go as simple or complex as you want. Add one layer, see where you stand, and add another if you think the design needs tweaking.
3D Printing Disadvantages
As with all things, 3D printing has its disadvantages, three of which are mentioned below:
- Slow production method → It’s true that 3D printing has a fast turnaround time, if you’re making 100 or less parts at a time. For mass production, this may not be the best route. If you run too many parts, you may risk the system altogether.
- No-go on large items → Whatever you have for a printing area is your max product size, which means you’re highly limited. If your particular design is hanging off the 3D printer even by ½ inch, the part will not function properly. So make sure you’re within the screens printing capabilities before you adopt this method.
- Rougher finish than desired → In theory, layer-by-layer printing sounds good, but it also gives off a rough finish. The details may be superb, but the feel to the plastic product may not be the greatest. Smoothing will be required, which may add another step to your assembly line process.
Injection Molding Advantages
When it comes to injection molding turnaround times, the plastic parts may take up to five to seven weeks just for simple parts to be produced. If you’re in the market to frequently change your overall design, this may not be the best use of your time and money.
On the bright side, injection molding is great once you nail down the design. High volumes (1000+ parts) go through in a streamline efficiency no matter how small or large the components are.
Additional advantages of injection molding include:
- Mass production → With the opportunity to use several molds at once, injection molding can really be cost-effective for any company.
- Great strength → Sometimes, a single layer of material is better than a layer-by-layer process. In this case with plastic parts, injection molding stands tall. Weakness will be the least of your concern.
- Little waste → Injection molding processes require someone to pour material directly into a mold, which means the supplies used for the design are almost exact. No waste accounted for means cost-efficiency and cost effectiveness.
Injection Molding Disadvantages
Just like 3D printing, injection molding has its disadvantages, laid out for you below:
- Limitations on design → Using a mold can mean that certain angles are unachievable, seeing as it would be too difficult to remove the plastic part without damage or breakage. The more complex the design, the less likely it will fit into an injection mold. The same goes for delicate designs.
- Limitations on change → With 3D printing, you’re able to change the design mid-way through production. With injection molding, that’s impossible. Once the design is finalized, it would be too tricky and costly to change the process and/or fix any mistake with the product. In a best case scenario, the current mold would have to be tossed and an entirely new mold would have to be made to fix any problem.
- Expensive entry → Injection molding is a very large investment and not something that should be gone into lightly. Prototyping, molds, materials, and systems cost upwards of six figures. If you’re looking to go the injection molding route, you’ll need to know for sure that the products you’re going to sell will be bought long term.